Diabetes is a chronic condition impacting millions worldwide, and managing it requires a careful and strategic approach. One aspect of diabetes management is ensuring that our foods are low in sugar and high in nutrients, which can sometimes be a challenge.
However, one fruit that has been gaining popularity among people with diabetes is kiwi. Kiwi fruit, also known as Chinese gooseberry, is a nutrient-packed fruit native to China but is now grown in many parts of the world, including New Zealand, Italy, and Chile.
Kiwi is known for its sweet and tangy taste, bright green flesh, and furry brown skin, making it visually appealing.
But what makes kiwis good for people with diabetes? Let’s explore the nutritional benefits of kiwi fruit, how it affects blood sugar levels, and what precautions people with diabetes need to take when consuming it.
So if you are a person with diabetes looking to add variety to your diet, please read more.
Nutritional Value of Kiwi Fruit Per 100g
Regarding healthy eating, kiwi fruit has emerged as a true superfood in recent years. This small, fuzzy fruit contains vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health.
Regarding nutrient content, kiwi fruit is particularly rich in vitamin C, crucial to immune function and skin health. It also contains vitamins K, E, potassium, and folate, all linked to various health benefits.
Other compounds in kiwi fruit, such as fibre and phytochemicals, may also help support digestive health and lower the risk of cancer and heart disease.
Following are the nutrient contents of the kiwi fruit as per the U.S Department of Agriculture:
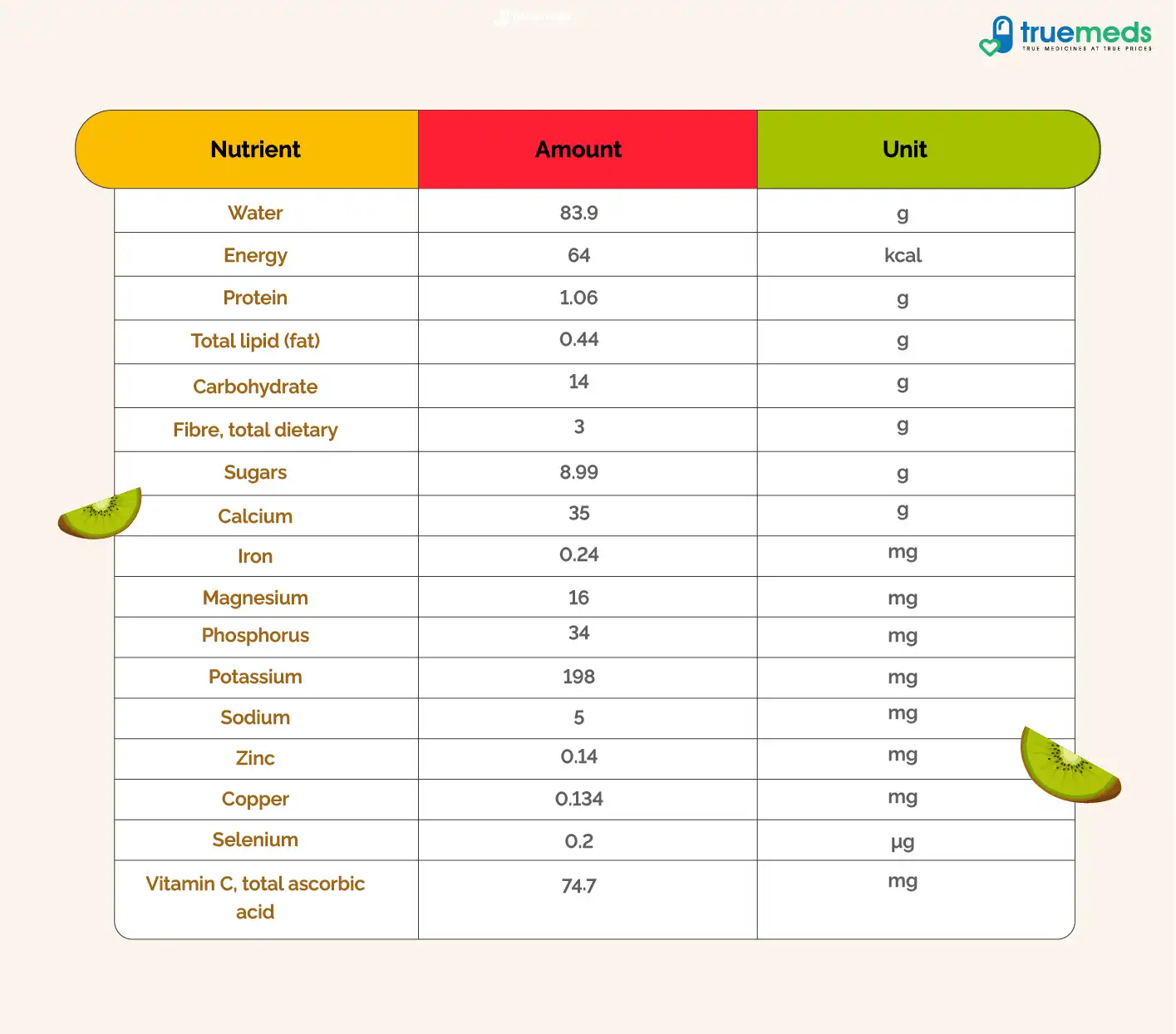
Kiwi fruit is a rich source of flavonoids known for their ability to combat free radicals and inflammation. These powerful antioxidants offer superior cell protection, making them nutritious. Enjoy the benefits of this exotic fruit without any guilt or second thoughts.
Glycemic Index of Kiwi Fruit
The glycemic index (GI) is valuable in determining how food impacts the body’s blood sugar levels.
Foods with a high GI are rapidly absorbed, leading to a quick surge in blood sugar. On the other hand, foods with a low glycemic index are digested at a slower pace, resulting in a more gradual and sustained increase in blood sugar.
This information can help individuals make informed choices about the foods they consume and their impact on overall health.
According to the statistics, kiwi has a moderate glycemic index (GI) value of 50, indicating that it is digested at a moderate pace.
When evaluating the impact of carbohydrates on blood sugar levels, it’s essential to consider both their quantity and quality. It is where glycemic load comes into play. Considering these factors, it provides a more accurate assessment of how consuming a particular food will affect blood sugar levels.
For example, the glycemic load of kiwi is 7.3, which is considered low. It means consuming kiwi is unlikely to cause a spike in blood sugar levels, thus making kiwis good for people with diabetes.
Is kiwi fruit safe for consumption by people with diabetes?
For individuals diagnosed with diabetes, maintaining stable blood sugar levels is of utmost importance. A reliable method for achieving this is to opt for foods with a lower glycemic index (GI).
One such food that should be considered is the kiwi fruit, which boasts impressive benefits. Notably, it has a moderate GI and is loaded with vital vitamins and minerals, including vitamins C and K, as well as potassium.
Furthermore, it is a rich source of dietary fibre that can help regulate digestion, making kiwis good for diabetics. Additionally, the kiwi fruit offers a light and healthy option, containing only 64 calories per 100-gram serving.
Incorporating kiwi fruit into the diet of individuals with diabetes can provide numerous health benefits. Nevertheless, it is crucial to balance it with other nutrient-dense foods, engage in physical activities, and take medication as directed.
Seeking the guidance of a healthcare provider or a nutritionist is highly recommended to develop a tailored eating plan that aligns with one’s specific health requirements.
Properties of Kiwi Fruit
Kiwi fruit boasts a range of beneficial properties that make it a valuable addition to a healthy diet. Rich in vitamin C, it supports immune function and skin health. The presence of vitamin K aids in blood clotting and bone health. Kiwi’s potassium content contributes to proper heart and muscle function. The fruit also contains antioxidants, including flavonoids, which help combat oxidative stress. With dietary fibre promoting digestive health and a combination of essential nutrients, kiwifruit offers a tasty and nutritious package for overall well-being.
Benefits of Kiwi Fruit for Diabetes Patients
Kiwi is a great addition to a diabetes diet chart due to its low glycemic index, high fiber content, and abundance of vitamins and minerals. Studies indicate that a single kiwifruit offers more than 100% of the recommended daily vitamin C intake and notable quantities of vitamin K and potassium. Additionally, it contains modest amounts of vitamins E, A, and folate.
Kiwi is rich in flavonoids, potent antioxidants that shield cells from free radical harm and potentially have anti-inflammatory effects. This small yet mighty fruit boasts several potential advantages, including the following.
List of 10 Benefits of Kiwi Fruit for Diabetes Patients
- Low Glycemic Index
- High Fibre content
- Rich Source of Vitamin C
- Blood clot prevention
- Helps with blood pressure regulation
- Promote digestive health
- Promote weight loss
- Suitable for skin health
- Good for heart health
- Reducing sugar absorption
1. Low Glycemic Index
Moderation is vital when consuming kiwi, as it has a glycemic index of 50 and is considered suitable food for those with diabetes. Pair it with a balanced diet and consistent physical activity to maximise benefits. What’s more, kiwi has been shown to slowly release glucose into the bloodstream, making kiwis suitable for diabetics and individuals managing gestational diabetes.
2. High Fibre content
Kiwis are a fantastic source of soluble and insoluble fibre, making them a valuable addition to any diet. Their high water retention capacity also assists in the absorption and digestion of sugars from various foods.
Moreover, studies indicate that incorporating fibrous foods can help regulate blood sugar levels, providing an added health benefit.
3. Rich Source of Vitamin C
Ensuring adequate Vitamin C intake promotes healthy tissue development and supports a robust immune system.
Additionally, it has been shown to effectively mitigate the harmful effects of uncontrolled blood sugar levels by reducing inflammation.
The production of collagen, essential for preventing diabetic dermopathy, is also boosted by Vitamin C. Since Kiwis are a rich source of this vital nutrient, incorporating them into one’s diet is a highly recommended strategy for maintaining optimal health.
4. Blood clot prevention
For individuals with diabetes, consuming kiwis can bring many advantages. These fruits are known to decrease the level of fat present in the bloodstream, which in turn helps to prevent the formation of dangerous blood clots. It is essential for those living with diabetes, as their elevated glucose levels can hinder the breakdown of these clots, potentially leading to an accumulation of plaque in the arteries.
By incorporating kiwis into their diet, individuals with diabetes can cultivate a healthier lifestyle and reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular complications.
5. Helps with blood pressure regulation
Incorporating kiwis into your diet may be beneficial for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and potentially preventing heart attacks and strokes.
A recent study found that consuming three kiwis daily over eight weeks decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure. This effect could be attributed to lutein, an antioxidant in kiwis that may help regulate blood pressure.
Kiwis’ high vitamin C content may contribute to these blood pressure-lowering effects.
Consider adding this nutritious fruit to your meals as a simple way to support your cardiovascular health.
6. Promote digestive health
Kiwi is an excellent addition to your diet to improve your digestion. This fruit is packed with dietary fibre known to be beneficial for digestive health. In addition to its high fibre content, kiwi contains an enzyme called actinic which can effectively break down proteins in the gut.
If you feel bloated after a heavy meal, consider eating a kiwi, as it can help break down proteins from meat and fish. It can ease discomfort and prevent bloating.
Furthermore, kiwis are known to have a mild laxative effect which can help to stimulate a sluggish digestive system. So if you’re looking for a natural way to promote healthy digestion, incorporating kiwi into your diet is worth considering.
7. Promote weight loss
Kiwis are a great addition to a weight-loss diet. Their high water content and low-calorie count make them an excellent snack choice. Plus, they’re a great ingredient for breakfast smoothies.
Vitamin C provides numerous health benefits, including regulating blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and gut health. The abundance of vitamin C in kiwis is essential for weight reduction.
8. Suitable for skin health
Collagen is vital in maintaining healthy skin and strong bones. It is necessary to consume enough collagen to support these vital functions of the body.
Kiwi, a fruit rich in vitamin C, can aid in producing collagen within the body. By consuming kiwis regularly, you can help maintain the structure and hydration of your skin, keeping it healthy and glowing.
Acne can be a frustrating and uncomfortable condition that affects many individuals. The anti-inflammatory properties and high vitamin C content in kiwis make them a natural remedy for reducing sebum production and inflammation in pores, which can help alleviate acne symptoms.
Read more – Healthy Diet for acne
For those looking to incorporate kiwi into their skincare routine, applying kiwi extract mixed with aloe vera to the skin and leaving it on overnight can provide excellent results. This simple and effective method can help nourish and rejuvenate your skin, leaving you feeling recharged and revitalised.
9. Good for heart health
Including various fruits and vegetables in your daily diet can significantly improve cardiovascular health.
Recent research suggests that kiwis may offer particular benefits in reducing risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure. In a study of 118 individuals with high, average, or stage one high blood pressure, those who ate kiwis or apples experienced positive effects on their blood pressure.
Of course, incorporating any fresh or frozen fruit into your diet can support your heart health, but kiwis are a tasty and effective option to consider.
10. Reducing sugar absorption
Consuming kiwi fruit is wise for people seeking to enhance their dietary fibre intake. The fruit’s fibre content aids in regulating blood sugar levels by slowing sugar absorption into the bloodstream, making kiwis good for diabetics. Furthermore, consuming fibre can positively impact digestive health and weight management, two crucial aspects for individuals with diabetes.
Side Effects of Kiwi Fruit
While kiwifruit is generally safe for consumption, some individuals may experience side effects. The high vitamin C content could lead to stomach upset or digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals. Additionally, some people may be allergic to kiwi, experiencing symptoms like itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Certain enzymes may irritate the mouth for some individuals. Consuming kiwi in moderation is advisable; be aware of any potential allergies. If adverse reactions occur, seeking medical advice is recommended. Enjoying kiwifruit in appropriate amounts can contribute to a healthy and balanced diet.
Ways to Enjoy Kiwi Fruit Diabetes Patients
Kiwi fruit boasts a range of health benefits, including aiding in bowel function, regulating blood pressure, and managing blood sugar levels. Luckily, numerous methods exist to integrate this nutritious fruit into your diet.
To reap the advantages of kiwi fruit, consider experimenting with various consumption methods. Each approach boasts distinct health benefits, allowing you to tailor your intake to your specific wellness needs.
- Kiwi + Cucumber salad: You can make a tasty and nutritious salad by combining kiwi fruit with cucumber, adding a tangy flavour to your dish.
- Kiwi as an evening snack: Dried kiwi fruit can be a healthy and satisfying evening snack that helps you feel fuller for longer.
- Kiwi Chutney: To add some spice to your meals, you can blend kiwi fruit with ginger, garlic, green chillies, and cilantro to create a zesty chutney that goes well with grilled chicken or fish.
- Kiwi raita: You can mix diced kiwi fruit with yoghurt and chopped mint to make a refreshing raita served as a side dish.
- Kiwi lassi: Blend fresh kiwi fruit and creamy yoghurt to create a delicious and versatile drink that can also be savoured as a delectable dessert.
Takeaway
In conclusion, kiwi fruit is an excellent addition to a diabetes-friendly diet due to its low glycemic index, high fibre content, and abundant vitamins and minerals.
Studies have shown that consuming kiwi fruit can help control blood sugar levels, promote digestion, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, making kiwis good for diabetics.
However, it is vital to remember that moderation is necessary, and people with diabetes should still monitor their intake and consult a dietician before adding kiwi fruit or any new food to their diet.
You can download our user-friendly Truemeds app for easy access. Submit your prescription to our platform to receive branded and generic medications. Enjoy savings on purchases and the added convenience of free home delivery on relevant orders across India*.
Kiwi fruit is generally considered to be suitable for diabetes and cholesterol management. It has a low GI, which means it does not cause a sudden increase in blood sugar levels. Kiwis are also fibre-rich, which promotes digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
While fresh kiwi is a healthy choice for people with diabetes, consuming it in moderation and as part of a balanced diet is essential. On the other hand, dry Kiwi may have a higher sugar concentration due to water removal, so diabetic patients should exercise caution and check the nutrition label before consuming dried fruits.
Diabetic patients should be cautious when consuming dried fruits, including dry kiwi, as removing water can result in a higher sugar concentration. It is recommended to carefully check the nutrition label and consider portion sizes before including dried fruits in the diet.
The exact mechanism by which kiwi lowers blood sugar has yet to be fully understood. However, it is believed to be attributed to dietary fibre, antioxidants, and various bioactive compounds that improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Both regular kiwi and gold kiwi can be included in a diabetic diet, but portion control is critical due to their natural sugar content. Gold kiwis have a slightly sweeter taste than regular kiwis, but they still offer similar benefits and can be relished as part of a well-balanced meal plan.
Suppose you have any specific concerns or dietary restrictions. In that case, consult with a doctor or a registered dietitian who can advise based on your needs and medical condition.
People with diabetes can generally include Kiwi fruit in their diet in moderation. It is advisable to consult a physician or a dietitian to determine the appropriate amount of kiwi to consume daily based on individual dietary needs and blood sugar management goals.
Drinking kiwi juice may lead to a quicker rise in blood sugar levels than a whole kiwi fruit, as the fibre content is reduced in the juice. It is recommended that people with diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels when consuming kiwi juice and consider the overall carbohydrate intake.
Kiwi fruit offers several health benefits due to its high vitamin C content, fibre, and antioxidants. It may help improve digestion, boost immune function, and support heart health. Some people may experience side effects such as allergic reactions or digestive discomfort. Awareness of any personal allergies or sensitivities to kiwi fruit is essential.
Kiwi fruit contains some iron and vitamin C, which can contribute to iron absorption and potentially support haemoglobin levels. However, it is not the sole solution for managing haemoglobin levels; balanced nutrition is essential.
There is no specific best time to eat kiwi fruit. Enjoy it as a balanced meal or snack throughout the day based on personal preferences and dietary needs.
Kiwi can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes and blood pressure concerns. It has a low glycemic index, meaning it doesn’t cause a rapid spike in blood sugar. The fibre in kiwi aids in blood sugar control, while potassium helps regulate blood pressure. However, moderation is key, and consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable.
Kiwi can be consumed anytime. Some prefer it as a snack, while others include it in breakfast or desserts. Eating it on an empty stomach may enhance nutrient absorption.
Kiwi glycemic index is low, making it a favourable choice for those monitoring blood sugar levels. The glycemic load accounts for a food item’s quality and quantity of carbohydrates.
Kiwi has natural sugars, but it is not considered high in sugar. Its sweetness comes along with fibre, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Enjoying kiwi in moderation can be a wise choice for those considering kiwi for diabetes management, thanks to its low glycemic index and fibre content.
Disclaimer
The content provided within this article has been thoroughly verified for accuracy. However, we advise consulting a healthcare professional before utilising any medication or dietary supplements mentioned herein.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6267416/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-HealthProfessional/
- https://diabetes.org/healthy-living/recipes-nutrition/eating-well/fruit
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/2344734/nutrients
- https://glycemic-index.net/kiwi/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1663443/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6267416/

Leave a Reply