Discovering the delicate interplay between insulin and glucagon is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being. These two hormones, each with their unique role, produce a precise balance to ensure your body’s energy needs are met efficiently.
This blog digs into the mechanisms of insulin and glucagon, shedding light on how they regulate glucose levels and prevent dramatic fluctuations. It will investigate their functions, responses to various situations, and the factors influencing their actions.
Whether you’re interested in diabetes management or simply curious about the marvels of your body’s internal processes, keep reading as we explain the cooperative collaboration of insulin and glucagon.
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a vital hormone produced by your pancreas, a small organ in your body. It acts like a key that helps your cells absorb sugar (glucose) from your blood. This sugar is your body’s primary source of energy.
When you eat, your blood sugar rises, triggering the release of insulin to facilitate the utilisation of this sugar by your cells as a source of energy. It also helps store any extra sugar as a backup for later. Insulin is vital in keeping your blood sugar levels steady and ensuring your body has the energy to function correctly.
Also read: Tips To Use Insulin
What is Glucagon?
Glucagon is another vital hormone produced by your pancreas, working alongside insulin. While insulin helps lower high blood sugar, glucagon does the opposite.
When your blood sugar gets too low, like when you haven’t eaten for a while, glucagon is released. It signals your liver to break down stored sugar and release it into your bloodstream. This raises your blood sugar levels, ensuring your body has enough energy.
Insulin and glucagon collaborate as a team, working together to uphold a balance in your blood sugar levels, ensuring your well-being and the proper functioning of your body.
Blood Glucose Regulation
Regulation of blood glucose levels is a crucial process that your body carefully manages to keep your energy levels steady and maintain overall health. When you eat, your body breaks down the food into sugars, which are then released into your bloodstream as glucose. Too much glucose can be harmful, so your body uses insulin to help move the excess glucose from your blood into your cells, where it’s used for energy.
Conversely, glucagon steps in when you’re not eating or your blood sugar drops. It signals your liver to release stored glucose into your bloodstream to prevent low blood sugar levels. This delicate interplay between insulin and glucagon ensures your blood sugar level remains within a healthy range. This balance is essential for your body’s energy needs and overall well-being.
Read Also: Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Factors Affecting blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can impact your blood glucose levels, affecting how high or low they go. Here are some key factors to consider:
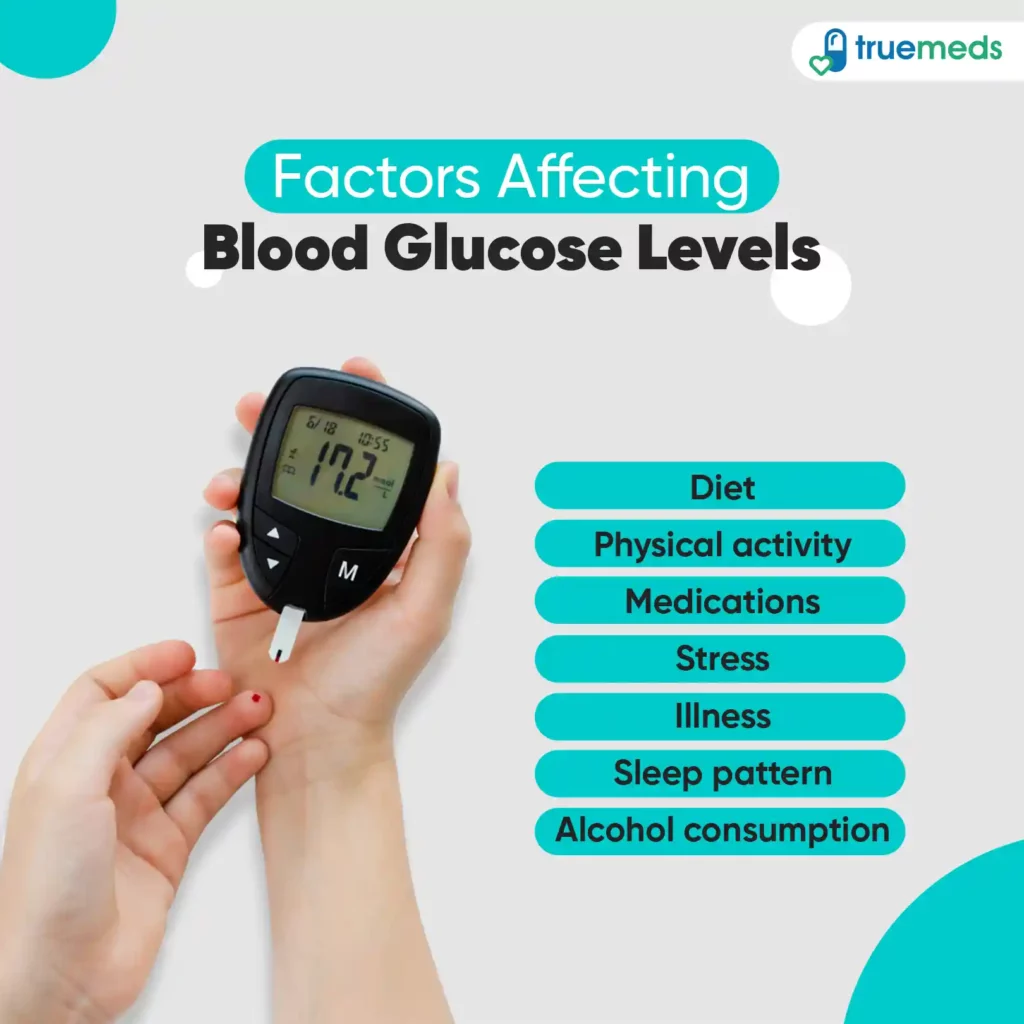
- Diet: The foods you eat play a noteworthy role. Carbohydrates, especially simple sugars, can quickly raise blood sugar levels. Fibre-rich foods and complex carbohydrates have a slower effect.
- Physical activity: Exercise helps your body use glucose for energy, which lowers blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, making it easier for cells to take in glucose.
- Medications: Insulin and other diabetes medications can directly influence blood sugar levels. Taking them as prescribed is essential to maintaining stable levels.
- Stress: The body’s stress hormones can increase blood sugar levels, resulting from the natural preparation for a “fight or flight” response.
- Illness: Infections and illnesses can trigger higher blood sugar levels as the body fights off the infection.
- Sleep: Poor sleep patterns can disrupt hormone regulation, affecting insulin sensitivity.
- Alcohol: Drinking alcohol can affect blood sugar levels, especially if consumed excessively.
Being mindful of these factors and making healthy lifestyle choices can effectively manage your blood glucose levels.
Read Also: What Level of Blood Sugar is Dangerous
Insulin and Glucagon Hormone Imbalance
An imbalance between insulin and glucagon hormones can affect blood sugar levels and lead to various health issues.
Insulin helps lower blood sugar by allowing cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. It stores extra glucose as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
Contrarily, glucagon works to elevate the glucose levels in the bloodstream. It effectively communicates with the liver to discharge the stored glycogen as glucose, which is utilised as energy as and when required.
When there’s an imbalance:
- Too much insulin: Your blood sugar can drop excessively, causing hypoglycemia.
- Too little insulin: Blood sugar can rise, leading to hyperglycemia, a hallmark of diabetes.
Imbalances can result from the following factors:
- Diabetes: Insulin deficiency leads to high blood sugar.
- Overactive glucagon: It can raise blood sugar too much.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Blood Glucose Levels
Maintaining healthy blood glucose is essential for overall well-being, especially for those managing diabetes or aiming for optimal health. Following a diabetes diet chart can help achieve this balance. Here are some helpful tips to keep your blood sugar in check:
1. Balanced diet: Focus on a well-rounded diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Monitor your carbohydrate intake and choose complex carbs over refined ones to avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar.
Also read: Juices for Diabetics Patients
2. Regular exercise: Engage in physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and aid in cell glucose uptake. Aim for a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises for optimal results.
3. Stress management: High stress levels can affect blood sugar. Practice techniques like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature to help reduce stress and keep blood glucose levels stable.
4. Proper sleep: Prioritise getting adequate and quality sleep. Sleep deprivation can impact insulin sensitivity and lead to irregular blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night.
Conclusion
Understanding the delicate interplay between insulin and glucagon is vital for maintaining blood sugar levels. These hormones work harmoniously to regulate glucose in your body, ensuring it’s available for energy when needed.
A healthy lifestyle, including a nutritious diet, regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient sleep, is pivotal in maintaining this balance. By making mindful choices and staying responsive to your body’s signals, you can support the intricate interplay of insulin and glucagon, promoting better overall health and preventing complications related to blood sugar imbalances.
You can download our user-friendly Truemeds app for easy access to medicine at low rates. Submit your prescription to our platform to receive branded and generic medications. Enjoy savings on purchases and the added convenience of free home delivery on relevant orders across India*.
Frequently Asked Questions
The function of insulin in the regulation of blood glucose levels is to help lower high blood sugar levels by facilitating glucose absorption into cells for energy or storage.
In gluconeogenesis, insulin suppresses it by inhibiting glucose production from non-carbohydrate sources in the liver. Glucagon, on the other hand, promotes gluconeogenesis, ensuring a steady supply of glucose when needed.
To increase blood sugar levels immediately, consuming sugary foods or drinks can provide a quick spike in glucose.
To control sugar levels immediately, consuming complex carbohydrates and proteins while avoiding high-sugar foods can help maintain stable blood sugar.
Insulin deficiency leads to increased blood sugar levels, resulting in diabetes mellitus.
The main differences between insulin and glucagon are their actions: insulin lowers blood sugar, while glucagon raises it. Also, they have opposite effects on glycogen storage and breakdown.
Diabetes mellitus is primarily caused by insufficient or ineffective insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Insulin isn’t administered orally because the digestive system breaks it down before reaching the bloodstream.
Insulin is produced by the pancreas, specifically by clusters of cells called beta cells located in the islets of Langerhans within the pancreas.
Glucagon is produced by the pancreas, specifically by alpha cells within the islets of Langerhans.
The three functions of glucagon are stimulating the liver to break glycogen into glucose (glycogenolysis), promoting gluconeogenesis, and encouraging the release of glucose into the bloodstream.
Insulin helps balance blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells for energy, thereby lowering blood sugar. It also signals the liver to store excess glucose as glycogen.
Glucagon raises blood sugar levels by prompting the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream, counteracting the effects of insulin.
Insulin resistance hinders the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, leading to higher blood sugar levels as glucose remains in the bloodstream instead of being absorbed by cells.
Disclaimer
The content provided within this article has been thoroughly verified for accuracy. However, it is advised to consult a doctor before utilising any medication or dietary supplements mentioned herein.
References
- Crecil Dias C, Kamath S, Vidyasagar S. Blood glucose regulation and insulin and glucagon infusion control using single model predictive control for type 1 diabetes mellitus. IET Systems Biology. 2020 Jun;14(3):133-46. [Cited on: 2023 August 7]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8687336/
- Ojha A, Ojha U, Mohammed R, Chandrashekar A, Ojha H. Current perspective on the role of insulin and glucagon in the pathogenesis and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clinical pharmacology: advances and applications. 2019 May 9:57-65. [Cited on: 2023 August 7]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6515536/
- Röder PV, Wu B, Liu Y, Han W. Pancreatic regulation of glucose homeostasis. Experimental & molecular medicine. 2016 Mar;48(3):e219-. [Cited on: 2023 August 7]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4892884/
Leave a Reply